Beiträge
https://www.nano-control.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/12/bunte-partikel-treten-als-emissionen-aus-einem-Laserdrucker-aus2.jpg
1120
1120
Heike Krüger
https://www.nano-control.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/05/Logo-nano-Control-Neu-mit-Schriftzug-300x126.png
Heike Krüger2024-12-28 19:04:442024-12-28 19:06:30Alle Jahre wieder Feinstaub
https://www.nano-control.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/10/xerox-laserdrucker-kleines-kind-im-nebel-282441990.png
1024
1024
Heike Krüger
https://www.nano-control.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/05/Logo-nano-Control-Neu-mit-Schriftzug-300x126.png
Heike Krüger2024-11-16 21:08:502024-11-16 21:12:53Indoor Air is Essential for Health:
Reliable, Clean Air to Breathe
https://www.nano-control.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/10/xerox-laserdrucker-kleines-kind-im-nebel-282441990.png
1024
1024
Heike Krüger
https://www.nano-control.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/05/Logo-nano-Control-Neu-mit-Schriftzug-300x126.png
Heike Krüger2024-10-24 17:29:452024-10-24 18:22:02Saubere Luft in Innenräumen ist existenziell für unsere Gesundheit: Wir wollen saubere Atemluft, auf die wir uns verlassen können
https://www.nano-control.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/Screenshot-Self-reported-Symptoms.jpg
1371
2268
Heike Krüger
https://www.nano-control.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/05/Logo-nano-Control-Neu-mit-Schriftzug-300x126.png
Heike Krüger2024-08-20 09:29:092024-09-02 16:50:43Self-reported symptoms associated with the use of printer and photocopier machines: Results from the nano-Control, International Foundation survey
https://www.nano-control.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/bild03_mann.jpg
296
317
Heike Krüger
https://www.nano-control.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/05/Logo-nano-Control-Neu-mit-Schriftzug-300x126.png
Heike Krüger2024-01-04 22:12:592024-01-04 22:29:47Es war für mich kaum vorstellbar, dass so alltägliche Gegenstände wie Laserdrucker oder bedrucktes Papier die Gesundheit schädigen können
https://www.nano-control.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/DSC00844-2.jpg
900
1500
Heike Krüger
https://www.nano-control.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/05/Logo-nano-Control-Neu-mit-Schriftzug-300x126.png
Heike Krüger2024-01-04 19:12:192024-01-06 14:27:37Ungerechtigkeit und Angst
https://www.nano-control.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/air-Q_canva.com_.jpg
500
750
Heike Krüger
https://www.nano-control.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/05/Logo-nano-Control-Neu-mit-Schriftzug-300x126.png
Heike Krüger2023-06-26 09:00:272023-06-26 11:40:41Schutz der Atemluft im Innenraum – denn für die Lunge gibt es keine Pille danach!


 nano-control - Playground KI
nano-control - Playground KI

 nano-Control
nano-Control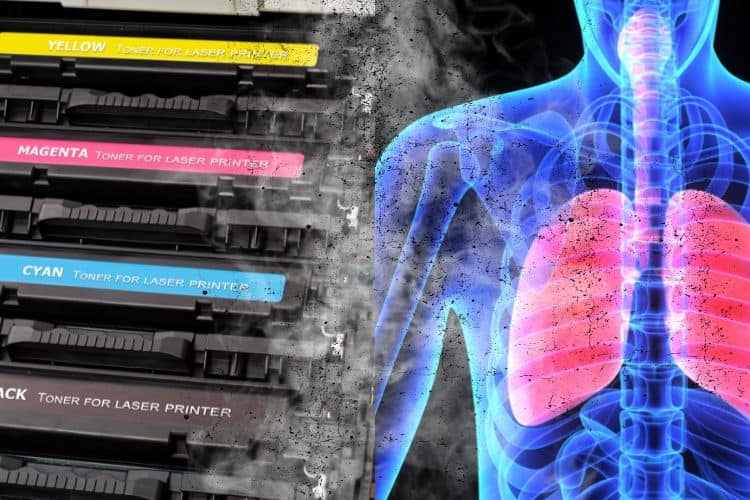 air-Q/Canva.com
air-Q/Canva.com